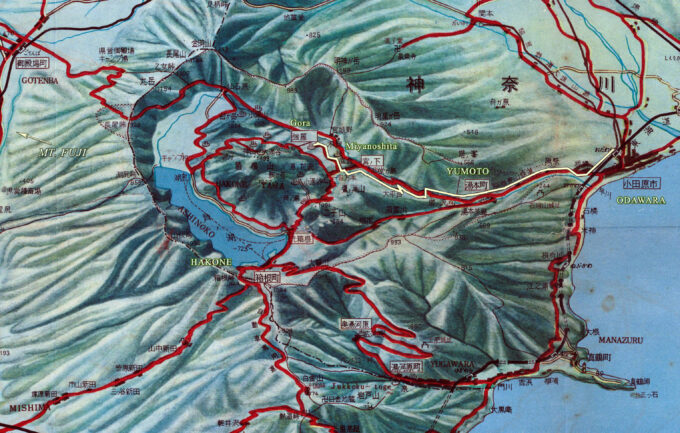
See also:
Mt. Fuji and Lake Hakone Railway Access and Bus Routes, c. 1930
“Abt system railway at Usui Pass”, Karuizawa, c. 1910.
Hot Spring Tea House at Tonosawa, c. 1920
Miyanoshita Village, Hakone, c. 1910
“[The] building of the Hakone Tozan Tetsudo illustrates why the potential offered by the new technology of electric traction was of particular utility in Japan. Electric cars were powered with an electric motor on each axle, while on a conventional steam-powered train only the driving wheels of the locomotive were powered.
“The grade … of one of several [Hakone Tozan] switchbacks indicate a grade of 8%. No steam locomotive could have climbed such a steep grade, unless it was cogged, as was the case of the slow-moving Abt rack locomotives used on the Usui Pass line, which averaged roughly 5 miles per hour.
“The electric cars of the Hakone regularly took this grade in stride and at speeds well in excess of the speeds that could be obtained on a rack railway.”
– Early Japanese Railways 1853-1914: Engineering Triumphs That Transformed Meiji-era Japan, by Dan Free, 2008
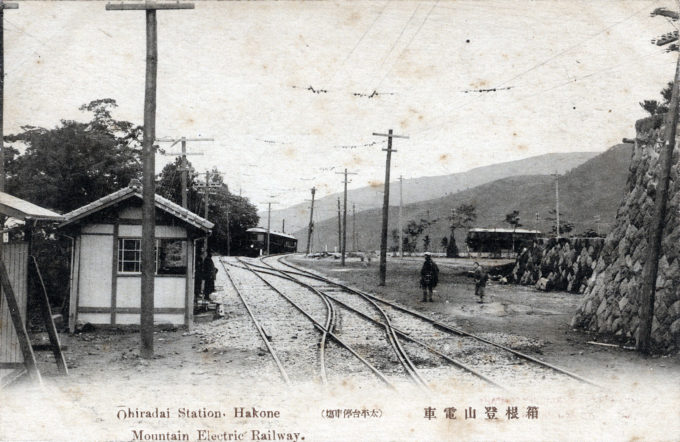
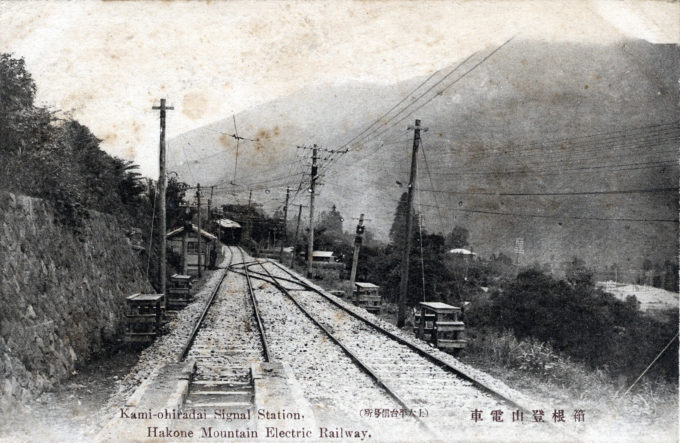
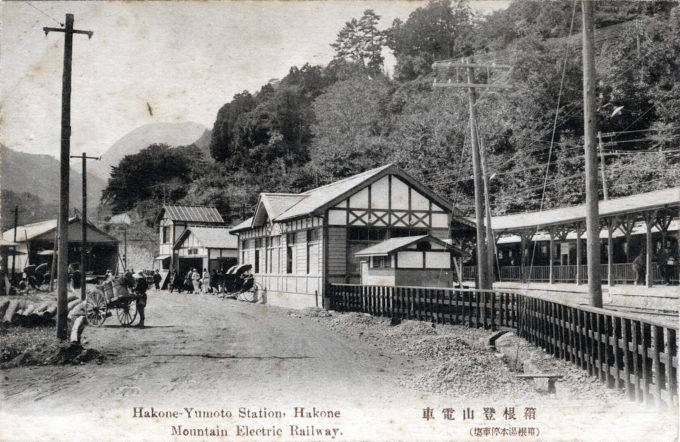
From the wiki: “Hakone Mountain Electric Railway Co. was founded in 1888 as the Odawara Horse-drawn Railway, operating from Kōzu Station (via Odawara Station) to Hakone-Yumoto Station. It underwent a name change in 1896 to Odawara Electric Railway before being renamed to the Hakone Tozan (lit. ‘Mountain Climbing’) Railway in 1928, and remains Japan’s oldest (and, now, the only) mountain railway.
“The line’s small trains pass through a narrow valley with thick forests, bridges, and tunnels; the route between Hakone-Yumoto Station and Gora Station features three switchbacks as it climbs the steep mountain, offering stunning views. Popular stations include the hot springs destinations of Tonosawa and Miyanoshita.
“The railway was electrified in 1900, replacing the original horse-drawn line; thru-service between Hakone-Yumoto and Gōra began in 1919 as an electric funicular railway; was connected to the Japan Government Railway’s Tokaido Main Line service at Odawara Station in 1920, resulting in the elimination of Kozu Station. The mainline railway was then extended from Hakone-Yumoto to Odawara in 1935.
“After World War II, Hakone Tozan Railway became a part of the Odakyu Group in 1948 with limited express and express ‘Romancecar’ service established from Shinjuku (Tokyo) connecting to the mountain railway at Hakone-Yumoto in 1950. In 2006, operations by Hakone Tozan using its own units was discontinued between Odawara and Hakone-Yumoto.”